Power Transmission Tower Equipment: Essential Components and Innovations
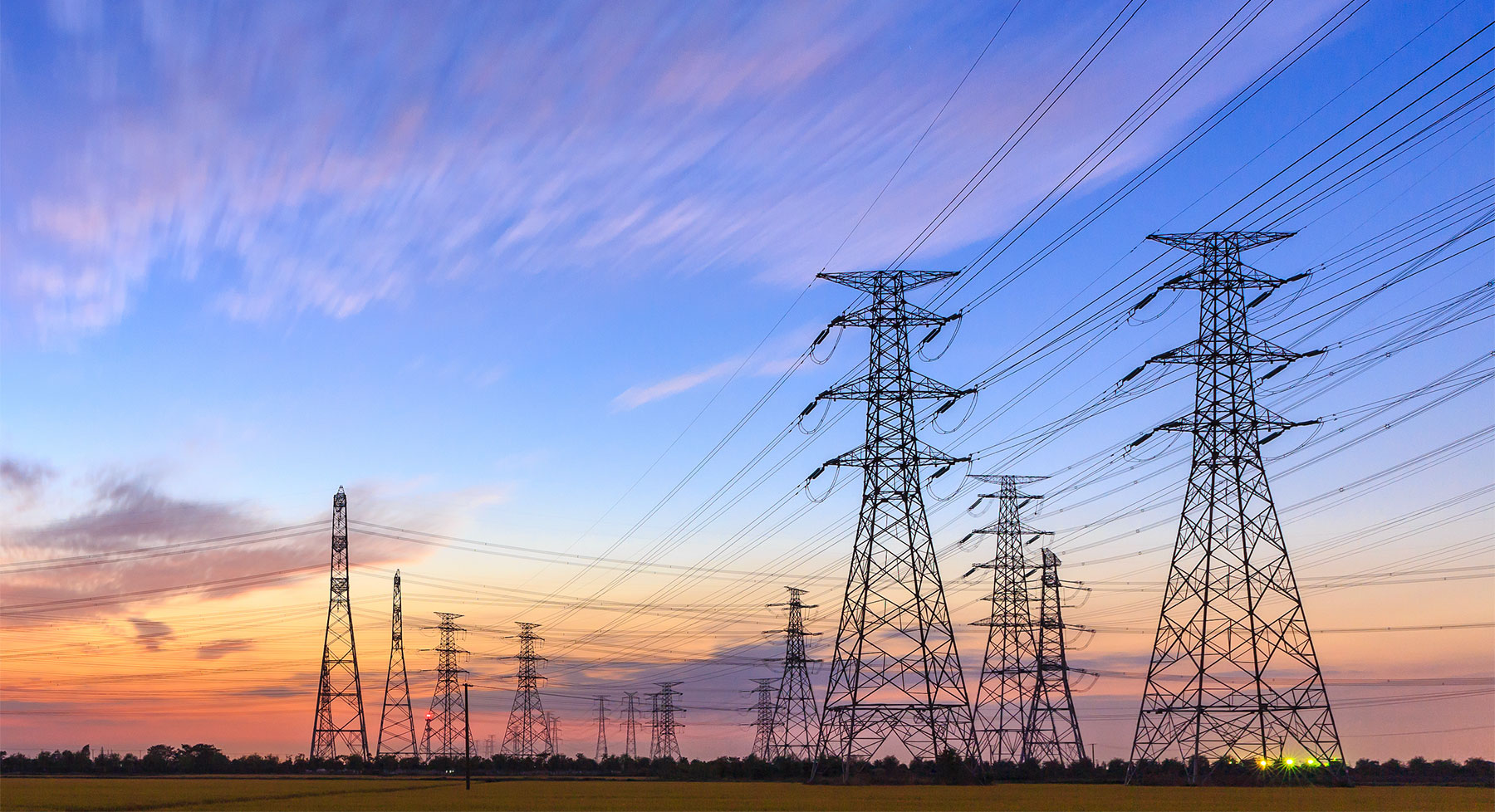
Power transmission towers are a vital part of the infrastructure that delivers electricity from power plants to consumers. These towering structures support high-voltage power lines, ensuring a reliable and efficient transmission of electrical energy across vast distances. In this post, we’ll delve into the key equipment and components that make up power transmission towers, as well as recent innovations in the industry.
Key Components of Power Transmission Towers
-
Tower Structure
- Materials: Traditionally, transmission towers are made from steel due to its high strength and durability. However, advancements in materials science are introducing composite materials that offer similar strength with reduced weight.
- Types: Different tower designs include lattice towers, monopole towers, and guyed towers. The choice depends on factors like the voltage of the transmission line, terrain, and environmental conditions.
- Lattice Towers: These are the most common type of transmission towers, characterized by their crisscrossed steel structures. They are highly stable and can support heavy loads.
- Monopole Towers: These towers consist of a single, tall pole and are used in areas where space is limited. They offer a sleek design and are easier to install.
- Guyed Towers: These are tall, slender towers stabilized by guy wires anchored to the ground. They are economical and can be quickly erected, making them suitable for remote locations.

Introducing Towerist Towerist is a leading producer of high-quality power transmission towers, offering a wide range of designs tailored to meet diverse needs. With a commitment to innovation and sustainability, Towerist utilizes advanced materials and engineering techniques to manufacture durable, efficient, and cost-effective transmission tower structures.
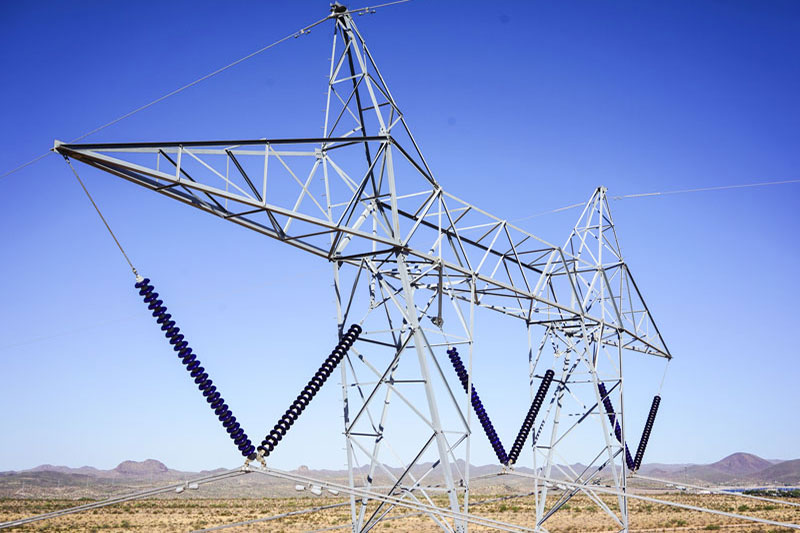
- Insulators
- Function: Insulators prevent the electrical current from traveling through the tower to the ground, ensuring the safety and efficiency of the transmission line.
- Types: Common types include porcelain, glass, and polymer insulators, each offering different benefits in terms of durability, performance, and cost.
- Conductors
- Materials: Conductors are typically made from aluminum or aluminum alloys, sometimes reinforced with steel. These materials provide an optimal balance between conductivity, strength, and weight.
- Configurations: Conductors are arranged in bundles to increase capacity and reduce losses due to the skin effect.
- Ground Wires
- Purpose: Ground wires (or shield wires) are installed at the top of transmission towers to protect the conductors from lightning strikes. These wires are grounded, providing a safe path for lightning to dissipate.
- Materials: Commonly used materials include galvanized steel or a combination of steel and aluminum.
- Tower Footings
- Foundation Types: The foundation of a transmission tower is crucial for stability. Different types include pad and chimney, grillage, pile, and raft foundations, chosen based on soil conditions and load requirements.
Innovations in Power Transmission Tower Equipment
The power transmission industry is continuously evolving, with innovations aimed at enhancing efficiency, reliability, and environmental sustainability.
- Composite Materials
- Benefits: Composite materials are being used to replace traditional steel components. They offer advantages such as corrosion resistance, reduced weight, and lower maintenance costs.
- Smart Grid Integration
- Technologies: Integration of smart grid technologies with transmission towers includes sensors and monitoring equipment that provide real-time data on the health and performance of the infrastructure.
- Advantages: These technologies enable predictive maintenance, reduce downtime, and improve the overall reliability of the power transmission network.
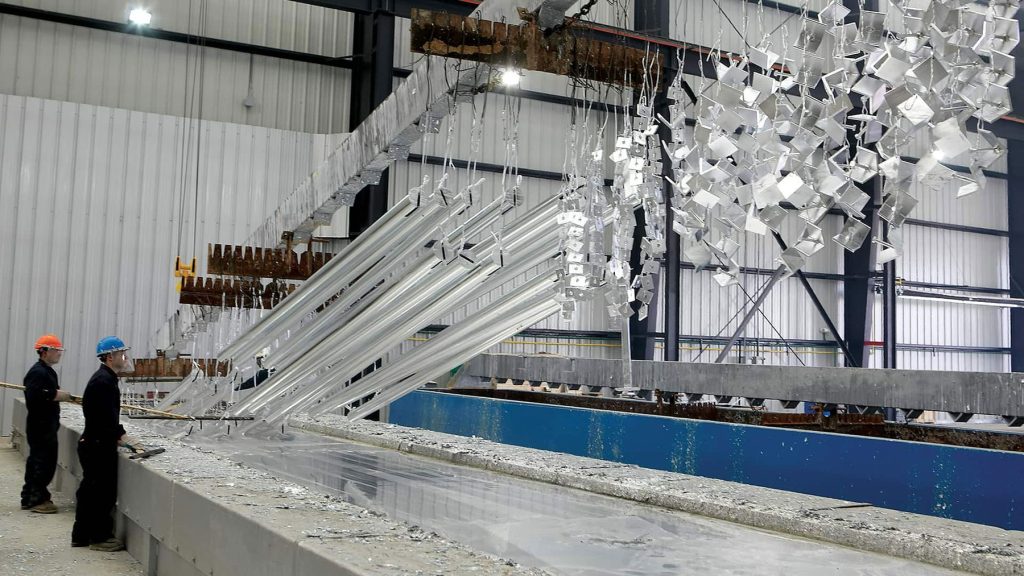
- Advanced Coatings and Treatments
- Protective Coatings: New coatings and surface treatments enhance the longevity of transmission towers by providing better protection against corrosion and environmental damage.
- Sustainable Solutions: Eco-friendly coatings are being developed to reduce the environmental impact of manufacturing and maintaining transmission towers.
- Modular Designs
- Flexibility: Modular tower designs allow for quicker and more efficient construction and maintenance. These designs can be easily adapted to different voltage levels and terrain types.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Modular systems reduce labor costs and construction time, providing a more economical solution for power transmission projects.
Conclusion
Power transmission towers are a cornerstone of modern electrical infrastructure, and the equipment used in their construction and maintenance is critical to their performance. By understanding the key components and embracing innovations in materials, technologies, and design, the industry can continue to improve the efficiency, reliability, and sustainability of power transmission systems.Stay tuned to our blog for more insights and updates on the latest trends and developments in power transmission tower manufacturing.