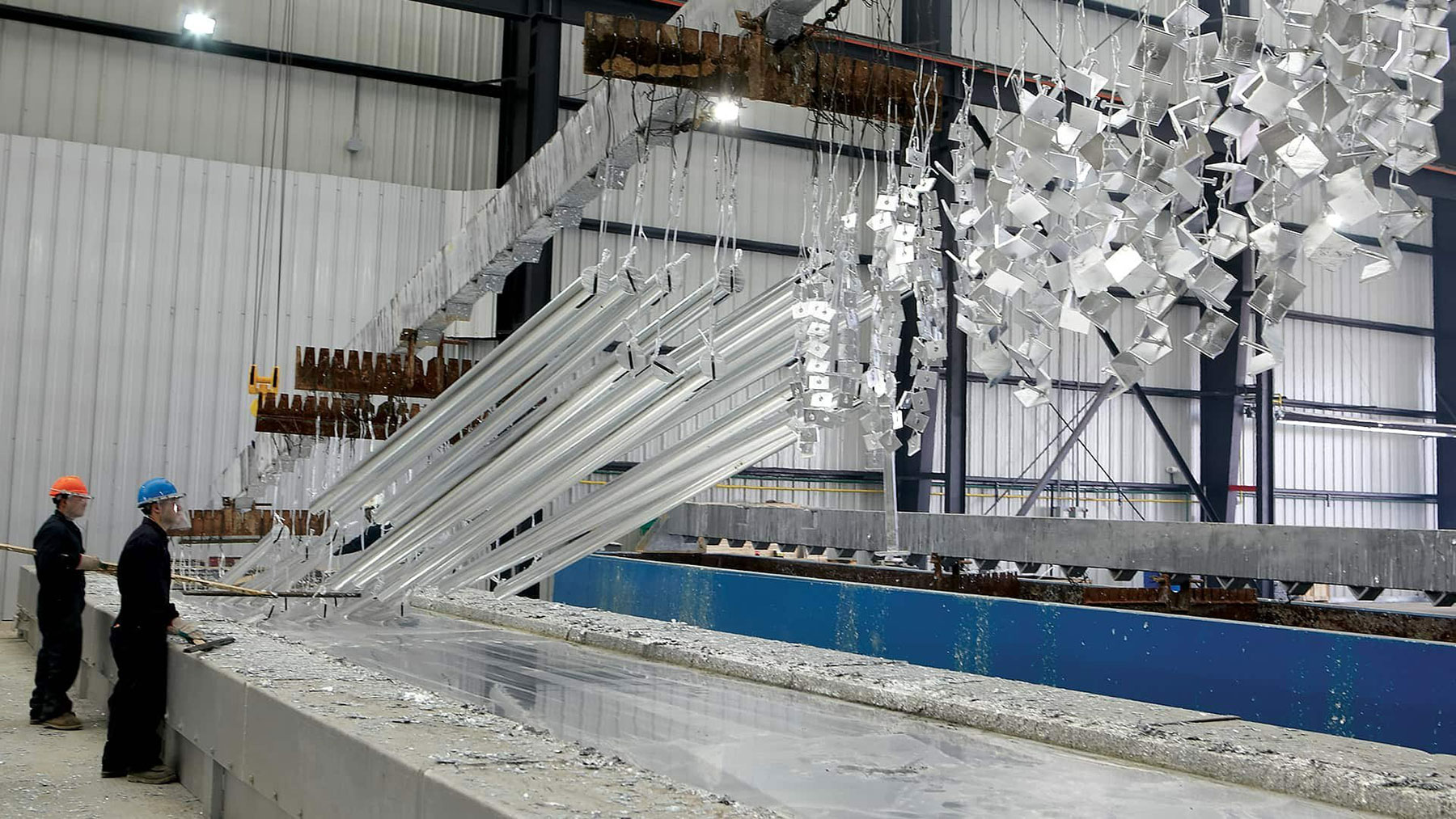
Types of galvanizing methods
Galvanizing, or galvanization, is a manufacturing process in which a zinc coating is applied to steel or iron to protect it against patina and rust. Several processes are available for galvanizing, but one of the most offered and used methods is called hot-dip galvanizing.
What is galvanized?
Galvanizing, or galvanization, is a manufacturing process in which a zinc coating is applied to steel or iron to protect it from patina and rust. A variety of galvanizing methods are available, but one of the most offered and used methods is called hot-dip galvanizing. Galvanized steel is one of the most popular types of steel due to its high durability, strength and malleability as well as corrosion protection of the zinc-iron coating. Zinc acts as a barrier against corrosive elements to protect the base metal, and the sacrificial nature of the coating results in a durable, high-quality steel product.
This versatility makes it usable for a variety of projects and industries, including agriculture, solar, automotive, construction, and more. In the following, Tower-ist provides a comprehensive description of how galvanized steel is processed, the types of galvanizing methods, its advantages, and how to use it in these different industries.
The galvanizing steps are as follows:
Steel is cleaned in a degreasing solution.
After cleaning, the steel is pickled by placing it in a container containing hot dilute sulfuric acid. The steel is then annealed in an aqueous solution (usually ammonium chloride).
After the flux, the steel is galvanized by immersion in a vat of molten metal. The steel is then checked for consistency and complete coverage.
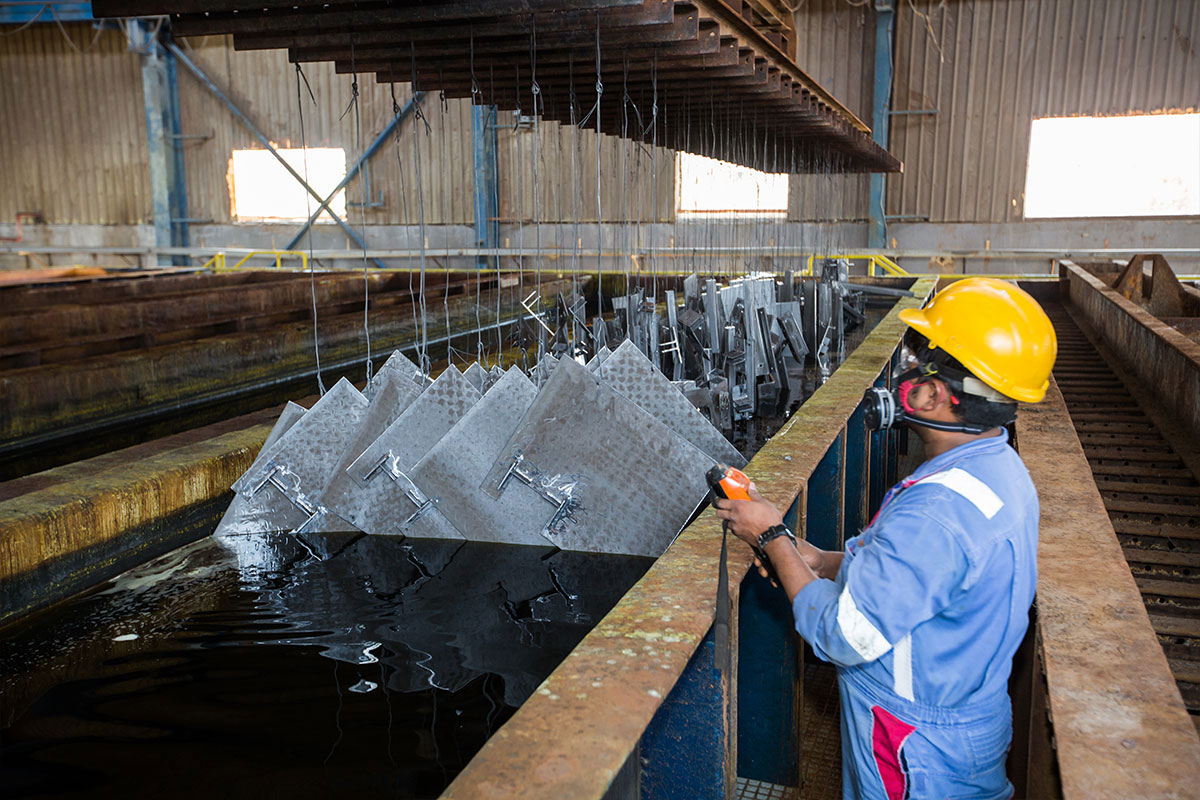

What are the advantages of galvanized steel?
Many different industries mostly they use galvanized steel because it has a wide range of advantages for the industries that can use them, including having:
- Low initial cost: Compared to most covered steels. In addition, galvanized steel is ready for use immediately after delivery. It does not require additional surface preparation, inspections and painting/covering, which saves companies more money.
- Longer life: With galvanizing, a piece of industrial steel can be expected to last 50+ years in moderate environments and 20+ years with heavy water exposure. No maintenance required. Increasing the durability of the final steel product also increases the reliability of the product.
- Rust resistance from zinc coating: The iron elements in steel are incredibly prone to rust, but the addition of zinc acts as a protective buffer between the steel and any moisture or oxygen. Galvanized steel is highly protective, including sharp corners and dents that cannot be protected with other coatings, and is resistant to damage.
Types of galvanizing methods
As mentioned above, there are several different processes for galvanizing steel which are as follows:
Hot galvanized
The first and most important method for galvanizing is hot-dip galvanizing. In this method, steel or iron is immersed in a pool of molten zinc, which is maintained at a temperature of about 860 degrees Fahrenheit (460 degrees Celsius).
This molten bath initiates a metallurgical bond between the zinc and the host metal. After the metal is pulled out of the bath, it reacts on exposure to the atmosphere and pure zinc mixes with oxygen to form zinc oxide. Zinc oxide further reacts with carbon dioxide to form zinc carbonate, which forms the final protective coating on the material.
A telltale sign of a hot-dip galvanized material is the presence of a crystal-like pattern on the surface, sometimes referred to as it is called “spangle”.
Hot-dip galvanizing is a cost-effective choice that can be quickly applied to simple and complex shapes.
The new coated material can be worked and machined in the same way as the uncoated material. Galvanized steel can be used in high temperature applications up to 392°F but use above this level will cause the zinc-carbonate layer to separate.
Galvanizing
Galvannealing is the result of combining the annealing and hot-dip galvanizing processes to produce a specialized coating on steel. The galvanizing process is done through instant and immersion annealing, which produces a matte gray finish.
Galvanized steel is a zinc-iron alloy product where the base metal is coated by a hot-dip process and then heated to create an alloy between the molten zinc coating and the steel. The resulting coating is a dull matte surface. Galvanized steel is suitable for welding and its surface is excellent for paint adhesion.
Pre-galvanize
This type of galvanizing is one of the highest ranges of galvanizing, but it is done in the first stage of production. Pre-galvanizing is a process that involves rolling sheet metal through a cleaning agent to quickly prepare the material for galvanizing. Then the metal is passed through a pool over the molten liquid and immediately recoils. The main advantage of this method is that steel sheet coils can be quickly galvanized on a large scale with a more uniform coating than the traditional hot dip method.
Electro galvanizing:
This method is one of the most unique methods of galvanizing, electro galvanizing does not involve immersing the material in a molten zinc container. Instead, an electric current is applied to an electrolytic solution applied to the steel, which reduces positively charged zinc ions to zinc metal. – which is then deposited on the positively charged steel. Like pre-galvanizing, this method is usually done in the first stage of production.
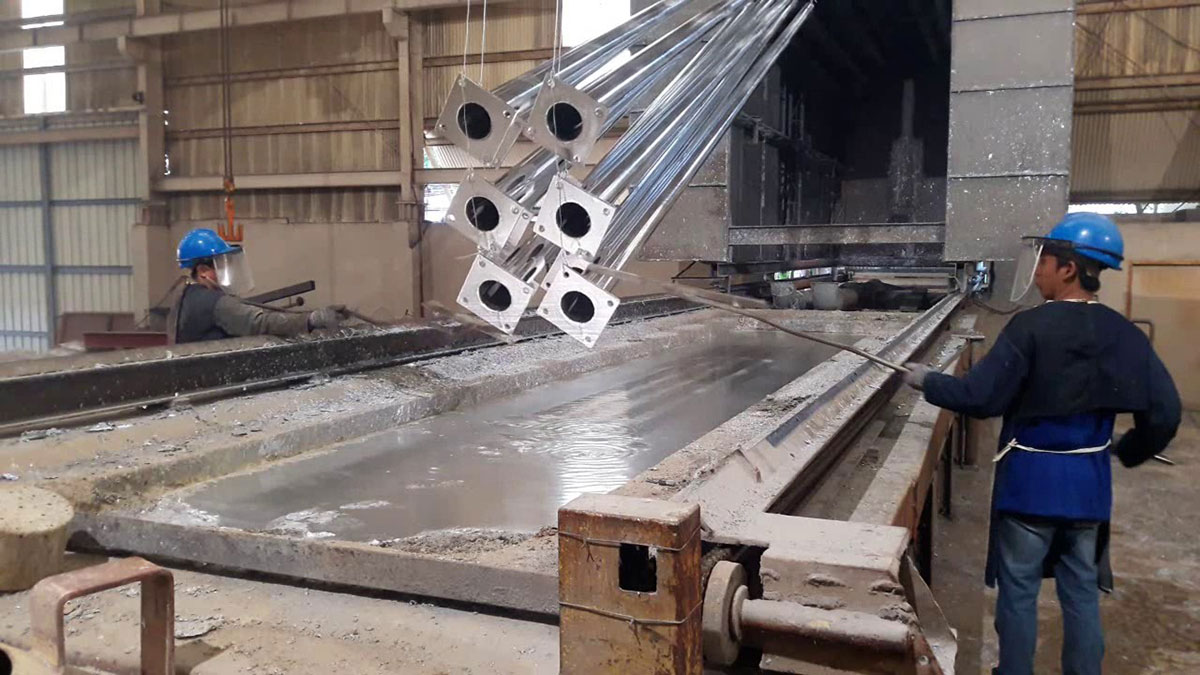

In what industries is galvanized steel used?
- Galvanized metals are used everywhere:
The bodies of cars and many bicycles are made of galvanized metal. Some drinking water pipes are still made of galvanized steel. Cold rolled sheet is also often galvanized.
- bolts, tools and all kinds of wire are now galvanized because it is an inexpensive process and helps extend the life of the metal.! Galvanized steel is often used in modern “steel frame” buildings. Galvanized steel is also used to create structures such as balconies, porches, staircases, ladders, corridors, etc. If your project will live outdoors after completion, galvanized metal is the ideal choice. Fences, roofs, outdoor walkways are all great choices for galvanized metal!
- Wind and solar industries: Solar projects must have continuous operation after installation and any repair/maintenance will result in service disruption. This means that hot-dip galvanized steels are popular in solar projects because of their corrosion protection. It is also popular for its “environmental” reasons as it produces no greenhouse gas emissions and guarantees decades of maintenance-free life. For example, it is often used in the agricultural industry because equipment is easily subject to corrosion, creating a demand for tougher and more flexible equipment. Hot-dip galvanized steel provides corrosion protection that can often last for decades, even when exposed to the harsh agricultural environment.
- Automobile industry: Although galvanized steel was only used in luxury models until the 1980s, the use of zinc-coated car bodies is now commonplace in the automotive industry. The “white body” of a car makes up about 80% of the body, all of which use galvanized steel. The rust resistance of galvanized steel is also a good marketing tool for the automotive industry because it can offer “rust-proof guarantees” to customers.
- Construction industry: Whether residential or commercial, the durability of galvanized steel has made it popular in the construction industry for over a century. It’s also chosen for construction because of its aesthetics. The “glow” of galvanized steel gives it a contemporary feel and is popular in modern architectural designs. Also, it’s not just used for large structural parts, but things like railings, gutters, rails, pipes, poles, and more.
- Telecommunication Industry: Maintaining of Tower Telecommunications is not easy, because they are tall and often difficult to reach. Hot-dip galvanized steel can be used on telephone wiring and equipment boxes, reducing the risk of damage and the need for maintenance.
With more than two decades of activity in the rigging industry.
Tower-ist Group has always been at the forefront in providing the best under the supervision of expert engineers.Also, all the materials in Tower-ist production units are of the best quality and have passed all the tests with the best results.