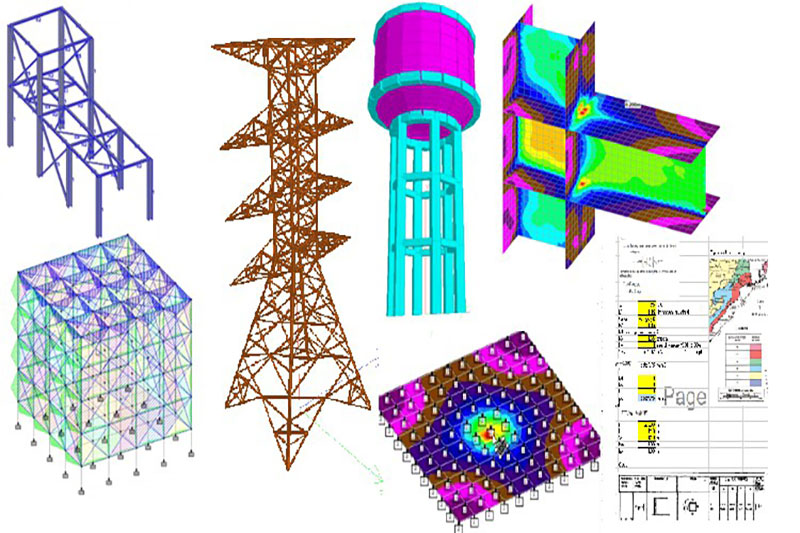
In the realm of power infrastructure, transmission towers stand tall as the unsung heroes, silently carrying the lifeblood of electricity across vast distances. Behind their towering presence lies a meticulous process of design and engineering aimed at ensuring reliability, efficiency, and safety. In this article, we delve into the intricacies of transmission tower design, exploring the innovative approaches and considerations that shape the backbone of modern power grids.
Understanding Transmission Tower Design
Understanding transmission tower design entails a comprehensive grasp of the intricate process involved in conceptualizing, planning, and engineering the structures that support overhead power lines. It encompasses a wide array of considerations, including structural integrity, electrical performance, environmental impact, maintenance requirements, and innovation.
Structural Integrity
Transmission towers must withstand various external forces, including wind, ice, and seismic activity, while supporting the weight of heavy conductors. Engineers meticulously calculate loads, analyze stresses, and select appropriate materials to ensure that towers remain stable and resilient under diverse conditions.
Electrical Performance
Beyond structural considerations, transmission tower design must optimize electrical performance. This involves determining the spacing and configuration of conductors, as well as implementing measures to minimize energy loss, maintain voltage levels, and ensure grid stability.
Environmental Impact
With growing concerns about environmental conservation, transmission tower design takes into account the ecological footprint of infrastructure. Designers strive to minimize visual impact, reduce land use, and integrate towers harmoniously into natural landscapes through innovative designs such as lattice towers or monopoles.
Maintenance and Accessibility
Ease of maintenance is a crucial aspect of transmission tower design. Engineers incorporate features such as access platforms, climbing systems, and corrosion-resistant materials to facilitate inspection, repair, and upkeep, thereby ensuring the long-term reliability of the infrastructure.
Innovation
Advancements in technology and materials drive innovation in transmission tower design. From the use of composite materials for enhanced durability to the integration of sensors and smart monitoring systems for real-time performance tracking, designers continually seek to improve efficiency, reliability, and sustainability.
In essence, understanding transmission tower design requires a holistic approach that considers not only the structural and electrical aspects but also the environmental, maintenance, and innovation factors that shape the evolution of power infrastructure. It is a multidisciplinary endeavor that demands collaboration among engineers, designers, environmentalists, and stakeholders to create solutions that meet the complex needs of modern society.
The Role of Experience
A Manufacturer’s Perspective
As a manufacturer with over twenty years of experience in telecommunications and electricity mast production, Towerist understands the critical importance of quality craftsmanship and innovative design in power infrastructure. With a proven track record of delivering robust and reliable mast solutions, we bring a wealth of expertise to the table in the realm of transmission tower design.
Designing power transmission towers requires a blend of technical knowledge from various disciplines to ensure the structures meet safety, reliability, and efficiency standards. Here are some key technical areas of expertise involved:
Structural Engineering
Structural engineers analyze loads, stresses, and dynamic forces acting on transmission towers to ensure they can withstand environmental factors such as wind, ice, seismic activity, and temperature fluctuations. They use principles of statics, dynamics, and structural mechanics to design tower components and support systems for optimal strength and stability.
Electrical Engineering
Electrical engineers focus on optimizing the electrical performance of transmission towers. They design conductor configurations, insulators, and grounding systems to minimize power losses, maintain voltage levels, and ensure grid stability. Understanding electrical properties such as resistance, capacitance, and inductance is crucial for designing efficient transmission lines.
Material Science
Knowledge of materials and their properties is essential for selecting appropriate materials for transmission tower components. Engineers consider factors such as strength, corrosion resistance, thermal expansion, and conductivity when choosing materials for towers, conductors, insulators, and hardware.
Geotechnical Engineering
Geotechnical engineers assess soil conditions and foundation requirements to ensure the stability of transmission tower foundations. They conduct soil tests, analyze bearing capacities, and design foundations capable of supporting the loads imposed by towers and conductors while minimizing settlement and soil displacement.
Environmental Engineering
Environmental considerations play a significant role in transmission tower design. Environmental engineers evaluate the impact of towers on ecosystems, habitats, and visual landscapes. They may design mitigation measures to minimize environmental disruption and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
Computer-Aided Design (CAD) and Modeling
CAD software and modeling tools are used extensively in transmission tower design to create detailed 3D models, simulate structural behavior, and analyze performance under different loading conditions. Engineers use these tools to optimize designs, identify potential issues, and refine structural components for efficiency and safety.
Regulatory Compliance: Knowledge of regulatory standards and codes governing the design and construction of transmission towers is essential. Engineers must ensure that tower designs meet industry standards such as ANSI/TIA-222 and ASCE 10, as well as local building codes and regulations related to safety, environmental impact, and land use.
Project Management
Effective project management skills are crucial for coordinating the design, procurement, construction, and installation of transmission towers. Engineers must manage timelines, budgets, resources, and stakeholder communications to ensure projects are completed on schedule and within budget while meeting quality and safety standards.
By integrating expertise from these technical disciplines, engineers can design transmission towers that meet the demanding requirements of modern power transmission systems, contributing to the reliability, efficiency, and sustainability of electrical infrastructure.
Conclusion
Transmission tower design is a testament to the intersection of art and science, blending aesthetic considerations with engineering precision to create structures that form the backbone of modern power grids. With a legacy of expertise and innovation, Towerist continues to be at the forefront of shaping the future of power infrastructure through cutting-edge design and manufacturing solutions. As we navigate towards a more sustainable and interconnected world, the evolution of transmission tower design will play a pivotal role in powering the aspirations of generations to come.