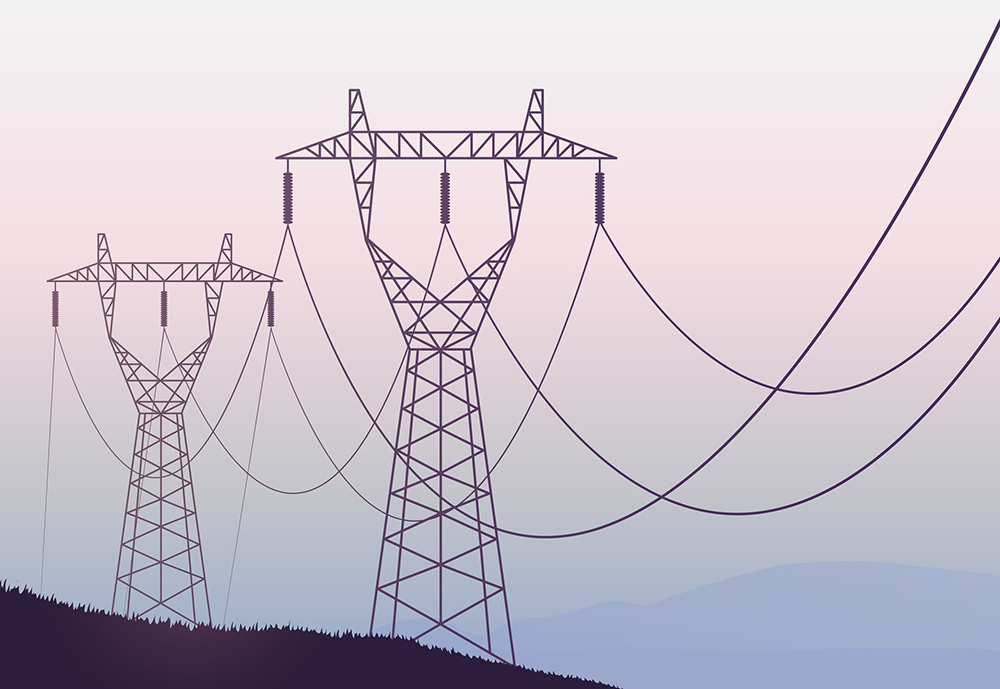
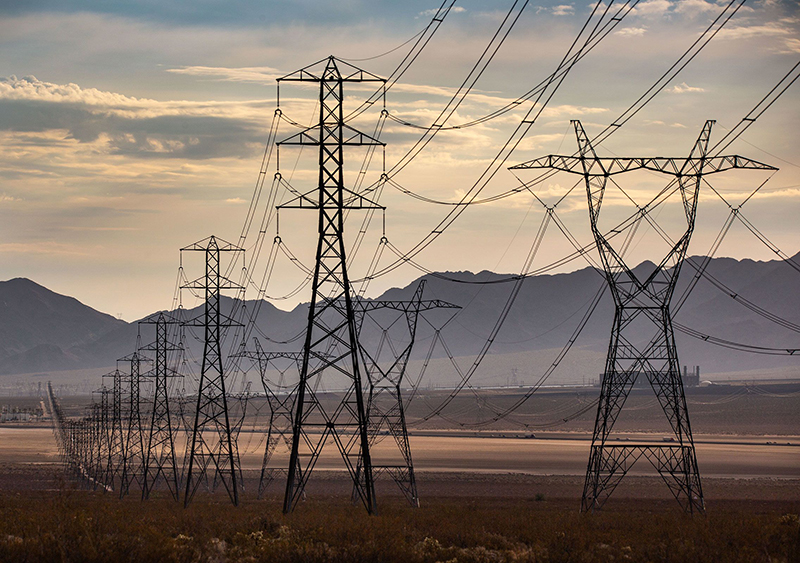
Why Are There 3 Transmission Lines?
In the world of electrical engineering and power distribution, you might have noticed that high-voltage transmission lines often come in groups of three. These three lines, known as a three-phase system, are essential for efficient power transmission over long distances. But why are there 3 transmission lines specifically? Let’s with towerist, delve into the reasons behind this configuration.
Understanding Three-Phase Power
Three-phase power is a method of electrical power transmission that utilizes three separate conductors. Each conductor carries an alternating current (AC) of the same frequency and voltage amplitude, but the currents are offset in phase by 120 degrees from each other. This setup is contrasted with single-phase power, which uses just one conductor and is common in residential settings.
for more reading: Are transmission towers AC or DC?
Advantages of Three-Phase Power
Increased Efficiency and Power Transfer:
Three-phase power is more efficient in transmitting electricity than single-phase power. It provides a more consistent and reliable power supply, which is crucial for industrial and commercial applications.
The power delivered by a three-phase system is constant, reducing pulsations and vibrations in motors and other machinery, leading to smoother operation and less wear and tear.
Balanced Load Distribution:
The three-phase system naturally balances the electrical load, reducing the amount of electrical energy lost during transmission. This balance also minimizes the risk of power outages and electrical faults.
Cost-Effectiveness:
Using three-phase power allows for smaller, lighter, and less expensive wiring and equipment. This is because the power carried by a three-phase system can be delivered using cables that are lighter and less expensive than those required for an equivalent single-phase system.
Transformers and other electrical devices can be smaller and more economical, leading to overall cost savings in both infrastructure and maintenance.
Technical Aspects of Three-Phase Transmission
Voltage and Current Characteristics:
In a three-phase system, the voltage in each conductor reaches its peak value at one-third of the cycle after the preceding conductor. This ensures that at any given time, one of the phases is always at its maximum voltage, providing a constant power supply.
The current in a three-phase system flows in a way that cancels out the magnetic fields generated by each phase, reducing losses due to electromagnetic interference.
Types of Three-Phase Configurations:
Delta Configuration (Δ): In this setup, the ends of each phase are connected in a triangle. Delta configurations are often used in high-voltage transmission lines because they can carry higher loads.
Wye Configuration (Y): In a Wye setup, one end of each phase is connected to a common neutral point. This configuration is typically used in distribution systems and allows for the use of a neutral wire, which can be useful for providing different voltage levels.
Applications of Three-Phase Power
Three-phase power systems are ubiquitous in various sectors, including:
Industrial and Commercial Facilities: Factories and large commercial buildings often rely on three-phase power for heavy machinery, HVAC systems, and elevators.
Power Generation and Distribution: Utilities use three-phase systems to generate and distribute electricity over long distances, ensuring stable and efficient power supply to cities and towns.
Electric Motors and Appliances: Many industrial motors and some high-power appliances are designed to operate on three-phase power due to its efficiency and reliability.
Conclusion
The use of three transmission lines in a three-phase system is a fundamental principle in modern electrical engineering, offering significant advantages in efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and reliability. By understanding why there are three transmission lines, we can appreciate the sophisticated design that powers our industries and homes, ensuring a steady and efficient flow of electricity across vast distances.
If you are involved in the planning, design, or maintenance of electrical systems, recognizing the benefits of three-phase power can help in making informed decisions that optimize performance and cost.
For more detailed information on electrical and telecommunication masts, visit our blog regularly. We provide in-depth articles and insights into the latest advancements and best practices in the industry.
References