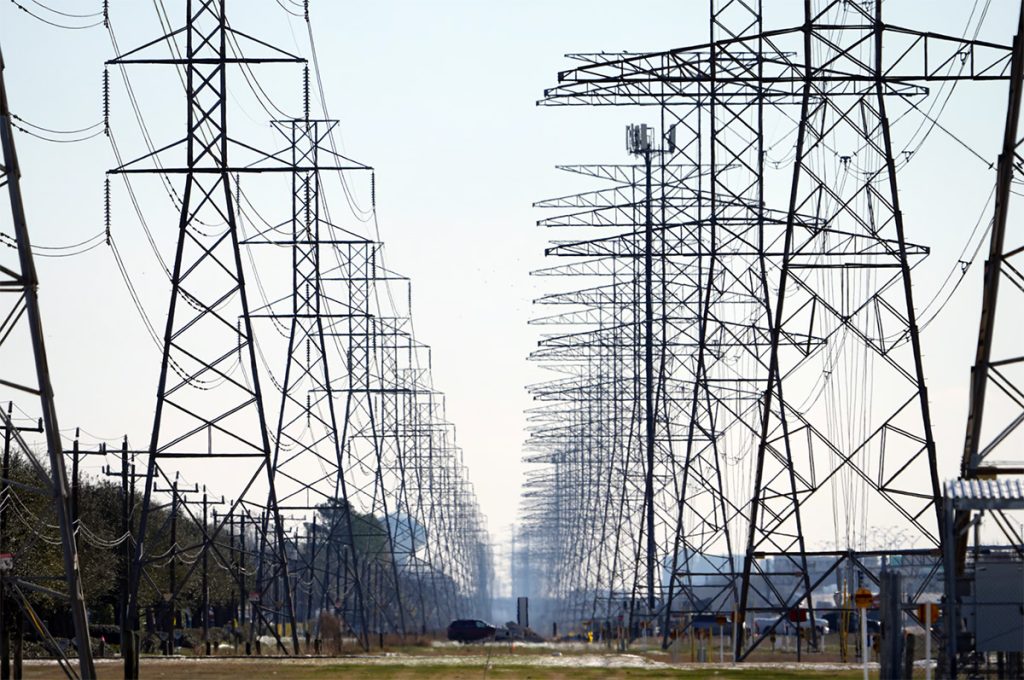
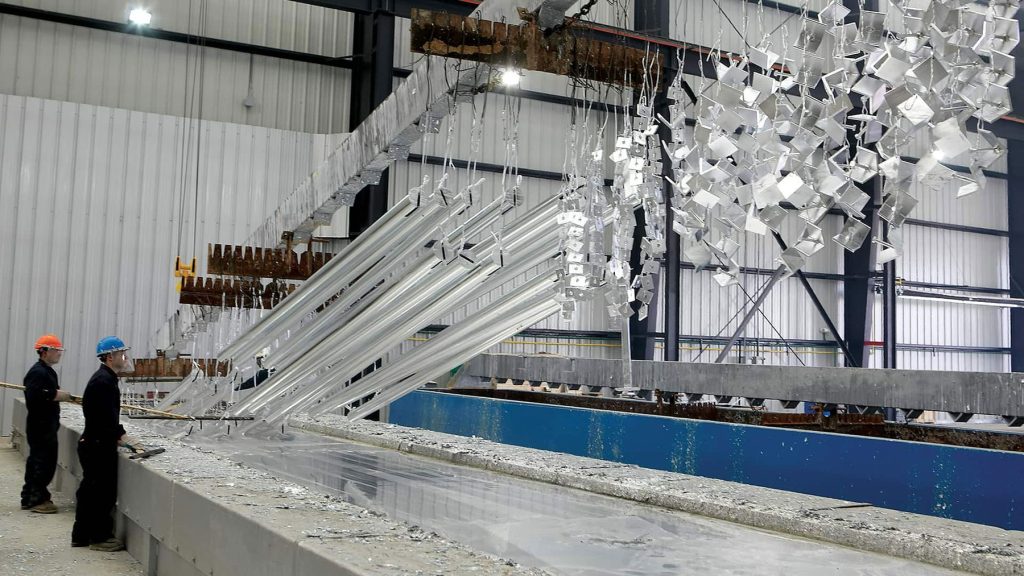
Power Transmission Tower Equipment: Essential Components and Innovations
Power transmission towers are a cornerstone of modern electrical infrastructure, and the equipment used in their construction and maintenance is critical to their performance. By understanding the key components and embracing innovations in materials, technologies, and design, the industry can continue to improve the efficiency, reliability, and sustainability of power transmission systems.Stay tuned to our blog for more insights and updates on the latest trends and developments in power transmission tower manufacturing.